New K2 Systems solutions in stock
In our Prague stock, we have many new PV mounting solutions from K2 Systems including TerraGrif earthing systems and cable routing solutions. Learn more about how to implement them in this article.
Equipotential bonding & earthing
What is equipotential bonding and earthing?
Equipotential bonding is achieved by conductively interconnected conductive points thus the electrical voltage between the points can no longer be measured.
The connection of a point on the electrical system to the ground is called earthing. This can fulfil certain tasks, such as:
Protection against the direct and indirect effect of an electric shock (personal protection).
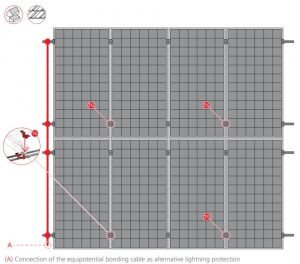
Lightning protection
Ensuring electromagnetic compatibility
Protective or functional earthing of certain equipment, such as power inverters
Equipotential bonding and an earthing system complement each other to form an effective protection system.
Equipotential bonding must always be added to PV systems in accordance with the specific national standard. This applies to all conductive and exposed components.
TerraGrif earthing system
Simple and fast module earthing solution for all K2 mounting systems
Complies with the earthing provisions in the standards NF C 15-100 and the guide UTE C15-712-1
Tested and approved by LCIE Bureau Veritas
Attention: For technical reasons, a TerraGrif cannot be used again after it has been used once and removed again. Please also check the TerraGrif assembly instructions.
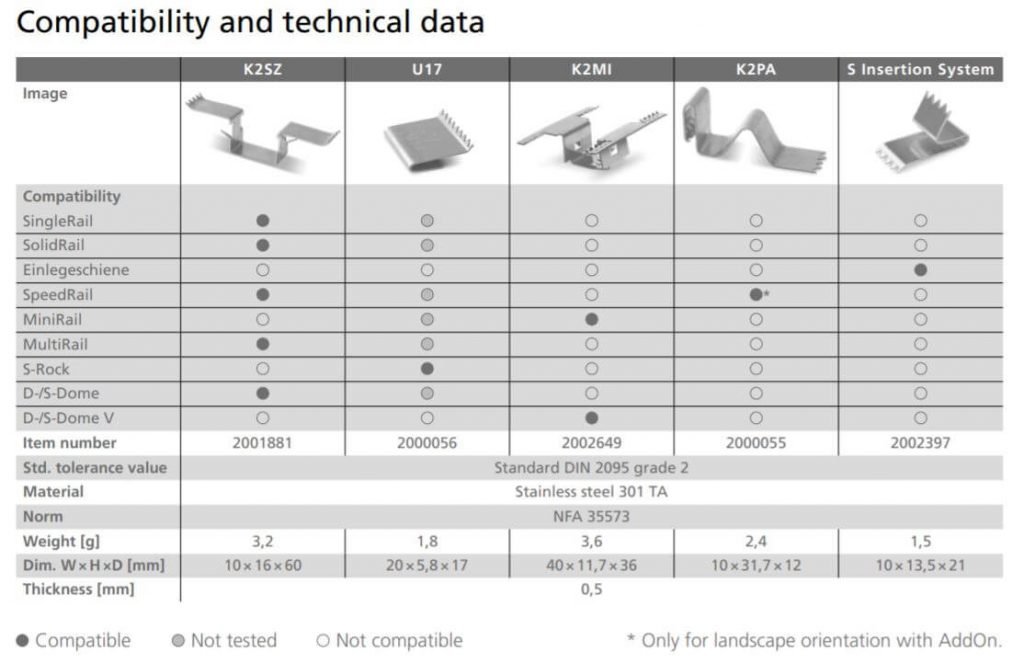
Overview of TerraGrif types for MiniRail, SolidRail and Dome V system:
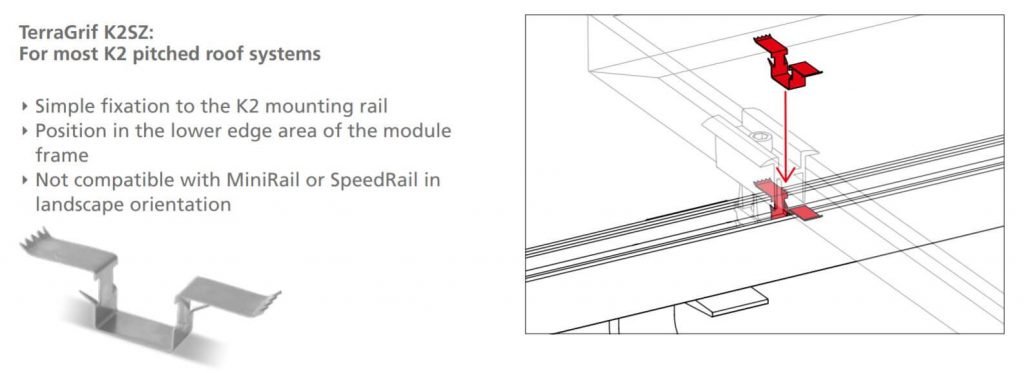
Tiled roof cover with the prescribed frame earthing (K2SZ)
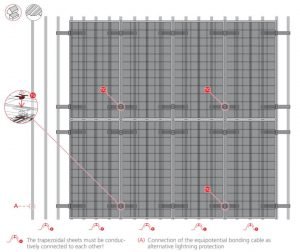
Trapezoidal metal sheet roof covers with MiniRail (K2SZ)
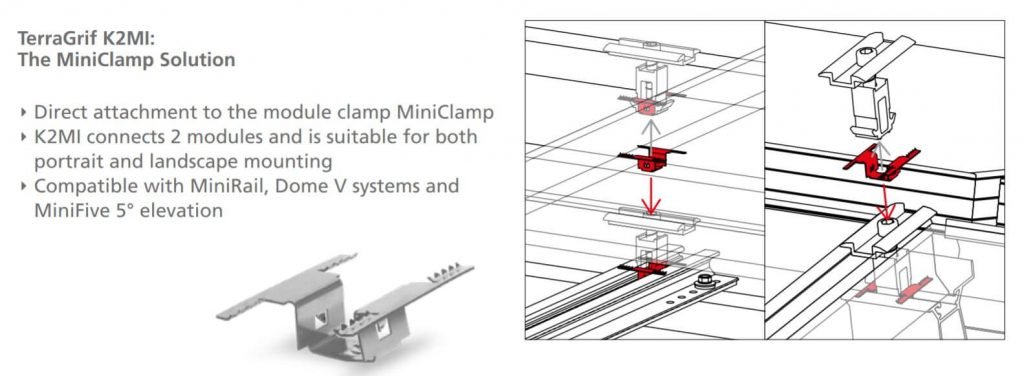
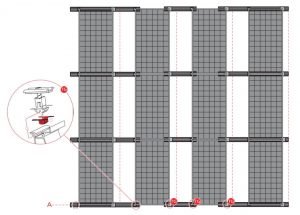
S-Dome V: Equipotential bonding (K2MI)
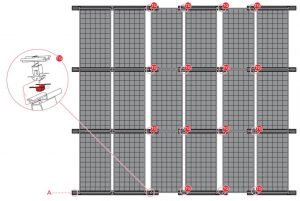
D-Dome V: Equipotential bonding (K2MI)

Subscribe to our newsletter
so that you don’t miss any news!
